JDBC
Model View Controller (MVC)
The MVC architecture pattern turns complex application development into a much more manageable process.
MVC stands for model-view-controller. Here’s what each of those components mean:
-
Model (data) The backend that contains all the data logic. The model’s job is to simply manage the data. Whether the data is from a database, API, or a JSON object, the model is responsible for managing it.
-
View (UI) The frontend or graphical user interface (GUI). The view’s job is to decide what the user will see on their screen, and how.
-
Controller (Brain) The brains of the application that controls how data is displayed. The controller’s responsibility is to pull, modify, and provide data to the user. Essentially, the controller is the link between the view and model.
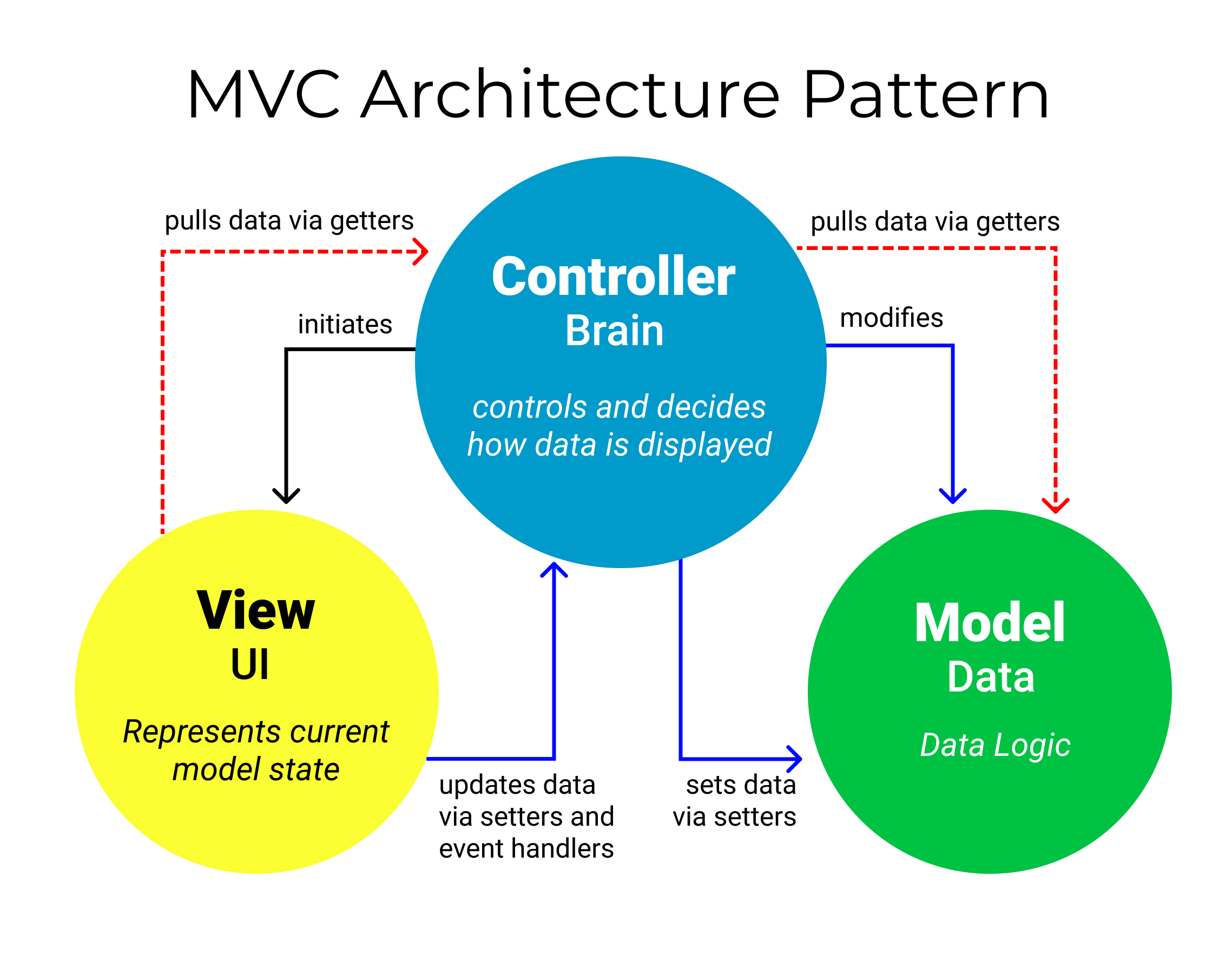
Today the MVC pattern is used for modern web applications because it allows the application to be scalable, maintainable, and easy to expand. The MVC pattern helps you break up the frontend and backend code into separate components. This way, it’s much easier to manage and make changes to either side without them interfering with each other.
Source: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/the-model-view-controller-pattern-mvc-architecture-and-frameworks-explained/