JDBC
JDBC in five minutes
This short tutorial provides an introduction to the JDBC interface, a driver for connecting Java programs with SQL-based databases, giving a sequence of steps to follow. In this course, we will work with an Access database.
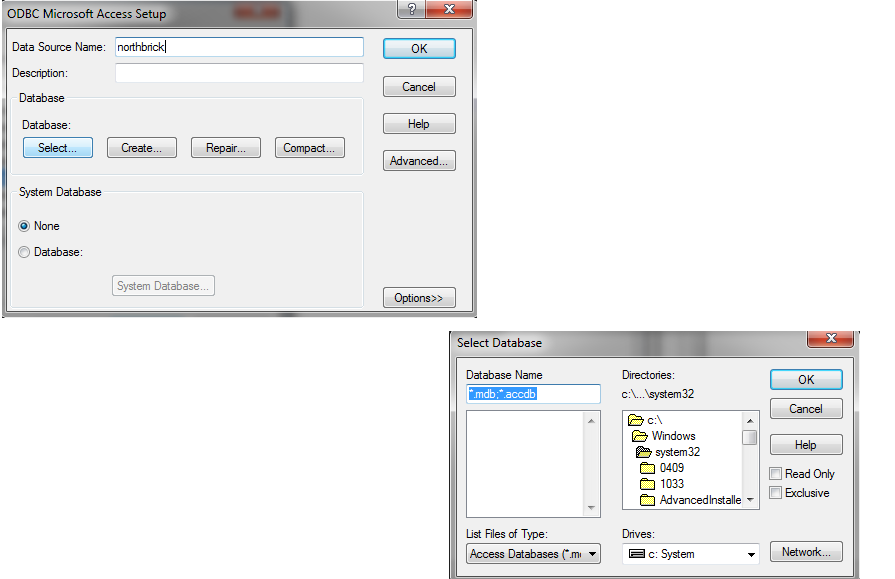
Step 1: Define a DSN (Data Source Name)
Important: if you do not see Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb, *accdb) in the list, go to the following folder C:\Windows\SysWOW64\odbcad.exe.
Step 1
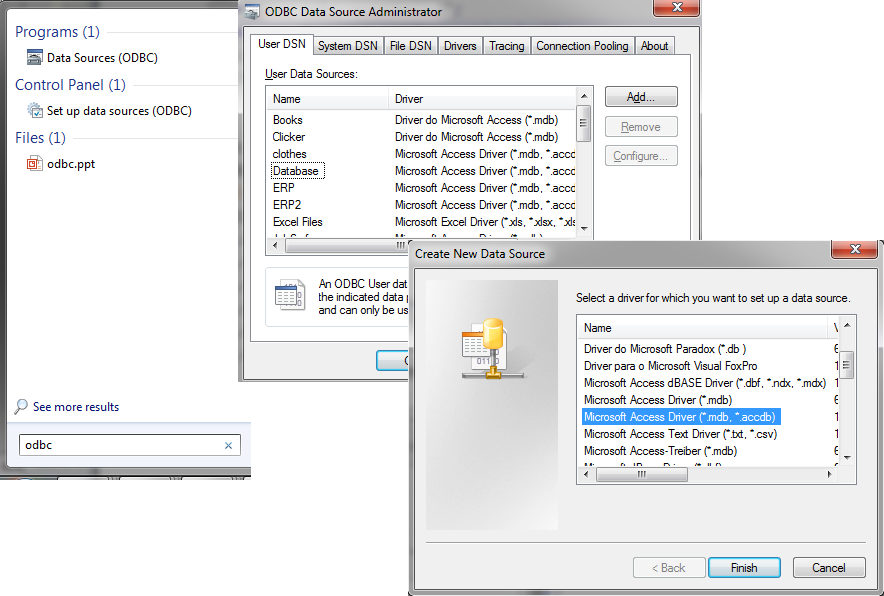 Step 2
Step 2
Step 2: Import libraries
In the Java file:
import java.sql.*;
Step 3: Load the driver
Class.forName( "sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver" );
Step 4: Obtain a Connection to the database
Connection connection = null;
String url="jdbc:odbc:northbrick";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
Step 5: Create a Statement object
Statement stmt;
stmt = connection.createStatement();
Step 6: Execute a query using a Statement
The Statement interface defines 2 methods for executing SQL queries:
1) public ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) returns a ResultSet that includes all rows and columns which match the SELECT query
ResultSet rs;
String query = "SELECT * FROM Authors";
// We recommend you to print the query before executing it
System.out.println("SQL: " + query);
rs = stmt.executeQuery( query );
2) public int executeUpdate(String sql) executeUpdate returns the number of rows changed by the update statement. This is used for insert statements, update statements and delete statements
String deleteStr = “DELETE FROM Authors WHERE LastName=‘Follet’";
int delnum = stmt.executeUpdate(deleteStr);
Step 7: Process the result (if it is a SELECT query)
Remember you have to use the next() function to point the cursor to the first row.
while (rs.next()) {
String s = rs.getString(“LastName”);
int y = rs.getInt(“YearBorn”);
System.out.println(s+” “+y);
}
Step 8: Close ResultSet and statement (if you don’t need them anymore)
rs.close();
stmt.close();
Step 9: Close the connection
Close the connection when you no longer need to access the database. The same connection object can be used to create further statements.
connection.close();
This is the final code:
import java.sql.*; //Step 2
class basicJDBC {
public static void main(String args[]) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver"); //Step 3
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:northbrick"); //Step 4
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement(); // Step 5
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("Select * from Shippers"); //Step 6
while(rs.next()) { //Step 7
System.out.print( rs.getString("CompanyName")+", ");
System.out.println(rs.getString("Phone"));
}
//Step 8
rs.close();
stmt.close();
//Step 9
connection.close();
}
}